CPT Codes Used for Chemotherapy Administration
Chemotherapy administration CPT codes describe the method, route and duration of drug delivery.
Core Chemotherapy Administration Code Range
96401–96549 – Chemotherapy and complex drug administration
These codes are not interchangeable with non-chemotherapy infusion codes.
Common Chemotherapy Infusion CPT Codes
Infusion coding depends on time and route of administration.
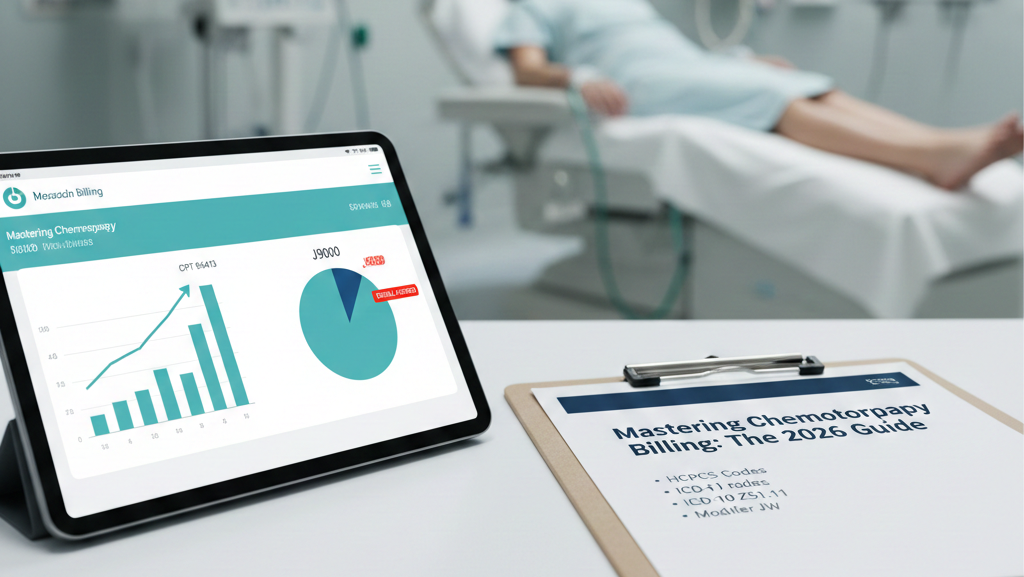
96413 – Initial intravenous chemotherapy infusion (up to 1 hour)
96415 – Each additional hour of IV chemotherapy infusion
Billing Rule:
Only one initial infusion code may be billed per visit, regardless of the number of drugs infused.
Chemotherapy Injection and Push Codes
96401 – Subcutaneous or intramuscular chemotherapy injection
96409 – IV push chemotherapy, initial drug
96411 – IV push, each additional drug
HCPCS Level II Codes for Chemotherapy Drugs
Chemotherapy drugs are reported using HCPCS Level II J-codes and Q-codes.
These codes identify:
- Specific cancer drugs
- Dosage units
- Brand or generic formulations
Examples of Common Chemotherapy Drug Codes
J9000 – Doxorubicin, 10 mg
J9267 – Paclitaxel, 1 mg
J9045 – Carboplatin, 50 mg
Drug Units and Dosage Calculations
Chemotherapy drug billing requires exact dosage reporting.
Example
If a drug code represents 10 mg per unit and the patient receives 120 mg:
Units billed: 12
Overstating or understating units is a leading cause of oncology claim denials.
ICD-10 Diagnosis Coding for Chemotherapy Claims
Diagnosis codes justify the medical necessity of chemotherapy services.
Common Cancer Diagnosis Codes
C50.919 – Malignant neoplasm of breast
C34.90 – Lung cancer, unspecified
C18.9 – Colon cancer
Encounter-Specific Code
Z51.11 – Encounter for antineoplastic chemotherapy
Best Practice:
List Z51.11 as the primary diagnosis, followed by the cancer diagnosis.
Medicare Guidelines for Chemotherapy Billing
Medicare Part B covers chemotherapy when services are:
- Medically necessary
- Properly documented
- Performed by enrolled providers
Key Medicare Requirements
- Accurate infusion start and stop times
- Drug wastage reporting
- National Drug Code (NDC) inclusion
- Compliance with CMS oncology policies
Failure to meet these requirements often results in audits.
Chemotherapy Drug Wastage Billing Rules
When single-dose vials are used, Medicare allows billing for discarded drugs.
Required Modifiers
JW – Amount of drug discarded
JZ – No drug discarded
Both modifiers require clear documentation in the medical record.
Modifiers Commonly Used in Oncology Billing
Modifiers help clarify chemotherapy claims.
59 – Distinct procedural service
25 – Separate E/M service on same day
JW / JZ – Drug wastage reporting
Documentation Requirements for Chemotherapy Services
Complete documentation protects reimbursement and compliance.
Records must include:
- Drug name and dosage
- Route of administration
- Infusion start and end times
- Lot number (if required)
- Medical necessity
Incomplete records increase audit risk.
Common Chemotherapy Billing Errors
Avoid these high-risk mistakes:
- Billing multiple initial infusion codes
- Incorrect drug units
- Missing Z51.11 diagnosis code
- Improper wastage reporting
- Billing non-covered oncology drugs
Oncology Billing and Revenue Cycle Management
Chemotherapy billing is a core component of oncology revenue cycle management.
- A strong RCM process includes:
- Provider enrollment with payers
- Charge capture accuracy
- Oncology-specific coding
- Claim follow-up and appeals
Effective RCM improves cash flow for cancer treatment centers.
Outsourcing Chemotherapy Billing Services
Many US oncology practices outsource chemotherapy billing due to its complexity.
Advantages of Specialized Oncology Billing
- Higher clean claim rates
- Reduced denial ratios
- Compliance with CMS guidelines
- Faster reimbursement cycles
Compliance Risks and Oncology Audits
Chemotherapy services face frequent payer scrutiny.
High-risk audit areas include:
- Infusion time overbilling
- Drug unit discrepancies
- Missing documentation
- Improper modifier use
Best Practices for Accurate Chemotherapy Billing
Train staff on oncology-specific coding rules
Verify payer drug policies regularly
Audit infusion documentation monthly
Use certified oncology coders
Why This Matters
Chemotherapy billing codes require precision, specialized knowledge and strict adherence to US oncology billing regulations. Accurate reporting of administration services, drug units, diagnosis codes and modifiers is essential for proper reimbursement.